软件与系统安全 - AFL 模糊测试实验
对 Coreutils 软件集合使用 AFL 进行模糊测试,撰写测试报告
在报告中详述:
(1)自己的整个实验过程(附必要截图)。
(2)第“三、1(2)”步骤的两种输入种子构造方法,对于 fuzzing 结果的影响(是否有影响?如果有,对最终获得的路径数量、路径数增长的速度等方面的具体影响)。
(3)第“三、1”基于编译插桩的 fuzzing 与第“三、2”的基于 Qemu 动态插桩的 fuzzing,从基本原理和实验效果两方面的差异。
[TOC]
一、实验环境
1 | OS: Ubuntu 20.04 focal |
二、实验准备
下载并安装 AFL
下载地址:https://github.com/google/AFL
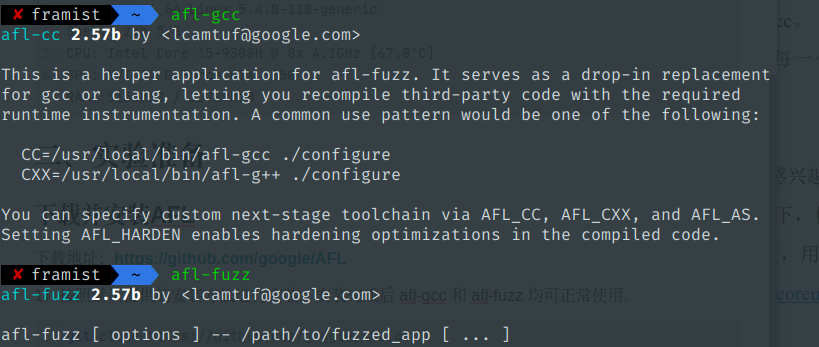
1)按照默认提供的安装方法进行安装,安装完成后 afl-gcc 和 afl-fuzz 均可正常使用。
1 | git clone https://github.com/google/AFL.git |
验证 afl-gcc 和 afl-fuzz 均可正常使用:
2)进入 qemu_mode 目录,使用 build_qemu_support.sh 脚本构建 FL-Qemu。
(可能需安装 libtool, libtool-bin 等依赖)。如 AFL-Qemu 安装存在问题,可预先安装 qemu
1 | sudo apt-get install libini-config-dev libtool-bin automake bison libglib2.0-dev qemu -y |
1 | /home/hxn/桌面/AFL_studio/AFL/qemu_mode/qemu-2.10.0/linux-user/syscall.c:261:16: error: static declaration of ‘gettid’ follows non-static declaration |
参考这个 issue:https://github.com/google/AFL/issues/41
使用这个项目代替:https://github.com/blurbdust/AFL(或者使用 google 更新的 patch 更好)
1 | get clone https://github.com/blurbdust/AFL.git |
之后按照上面的步骤进行安装。
出现这个就说明安装成功了:
1 | [+] Build process successful! |
下载目标程序集(coreutils-9.1.tar.gz)
下载地址:https://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/coreutils/
1 | wget https://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/coreutils/coreutils-9.1.tar.gz |
三、实验步骤
1. 基于编译器的目标程序插桩
(1)使用 afl-gcc,生成 coreutils 的每个二进制程序,具体步骤为:
a)查看 coreutils 的 configure 选项,指定 cc=afl-gcc。
1 | ./configure CC=afl-gcc |
这一步一般用来生成 Makefile,为下一步的编译做准备,你可以通过在 configure 后加上参数来对安装进行控制,比如代码:
./configure --prefix=/usr上面的意思是将该软件安装在 /usr 下面,执行文件就会安装在 /usr/bin.同时一些软件的配置文件你可以通过指定 –sys-config= 参数进行设定。有一些软件还可以加上 –with、–enable、–without、–disable 等等参数对编译加以控制,你可以通过允许 ./configure –help 察看详细的说明帮助
b)生成 coreutils 二进制程序集。make 出来的每一个插桩后二进制均在 coreutils-9.1/src 目录下。
1 | make |
(2)为 coreutils 的特定程序确定输入种子
coreutils 包含很多二进制程序,自己从中选择 3 个感兴趣的程序进行 fuzzing。
构造输入种子列表,存放于 coreutils-9.1/src/input 目录下,构造方法可以选择:
a)学习 coreutils 文档中这 3 个程序的命令行选项,用这些命令行选项构建
(文档见 https://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/manual/coreutils.html)。
b)直接用随机构造的任意字符串作为输入种子。
1 | mkdir input |
(3)在 coreutils-9.1/src 目录下,使用 afl-fuzz -i input -o output ./[程序名] @@进行 fuzzing,一段时间后终止 fuzzing 并在 coreutils-9.1/src/output 目录下查看测试结果。
出现的问题大都可以按提示进行修复
1 | [-] Hmm, your system is configured to send core dump notifications to an |
解决方法:
1 | su |
出现问题:
1 | Whoops, your system uses on-demand CPU frequency scaling, adjusted |
解决方法:
1 | su |
出现问题:
1 | [-] SYSTEM ERROR : Unable to create './output/queue/id:000000,orig:gif.dict' |
推测是文件系统的问题,目前运行在 NTFS 中,复制整个工程到 Linux 系统盘上试试。
1 | afl-fuzz -i input -o output ./od -x @@ |
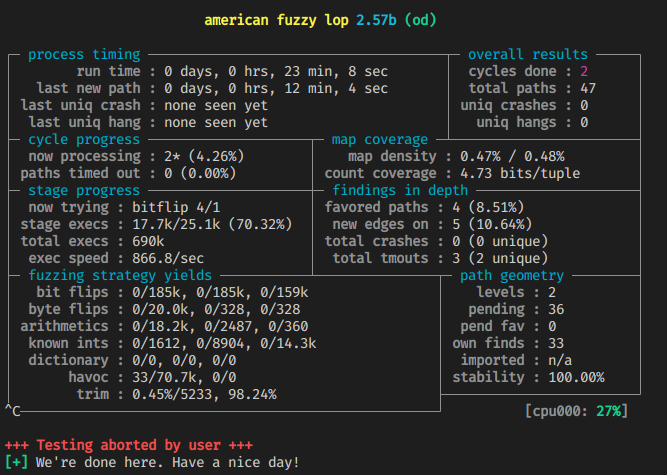
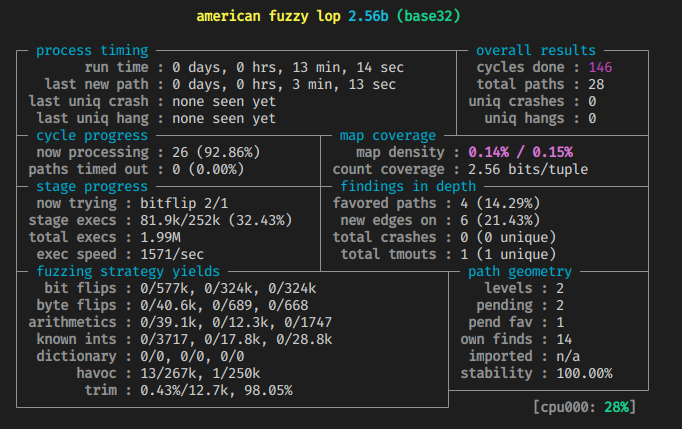
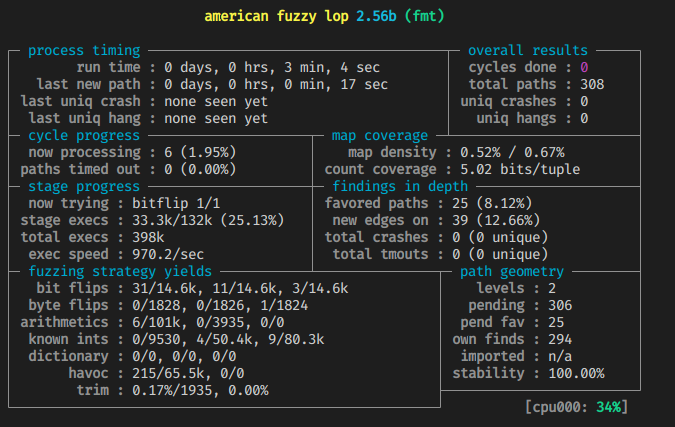
https://www.cnblogs.com/unr4v31/p/15237728.html
什么时候可以停止 fuzzer?其中一个指标可以参考
cycles done的数字颜色,依次会出现洋葱红色,黄色,蓝色,绿色,变成绿色时就很难产生新的 crash 文件了。
2. 基于 AFL-Qemu 的目标程序动态插桩
(1)重新生成 coreutils 的每个二进制程序(不使用 afl-gcc,而是用默认 gcc 进行 configure/make)。
1 | ./configure |
(2)使用 afl-fuzz 的 -Q 选项,对你的 3 个 coreutils 程序进行 fuzzing。构造输入种子的方法同上。
1 | afl-fuzz -Q -i input -o output od -x @@ |
可以看出相比直接插装要慢好多
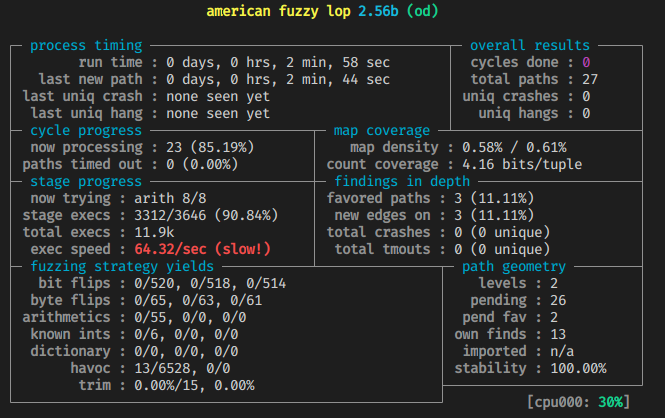
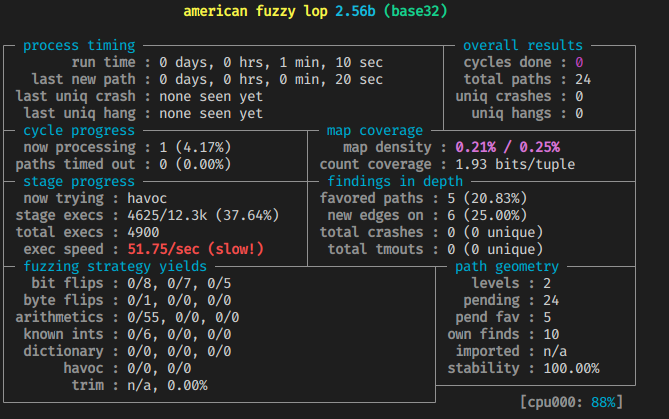
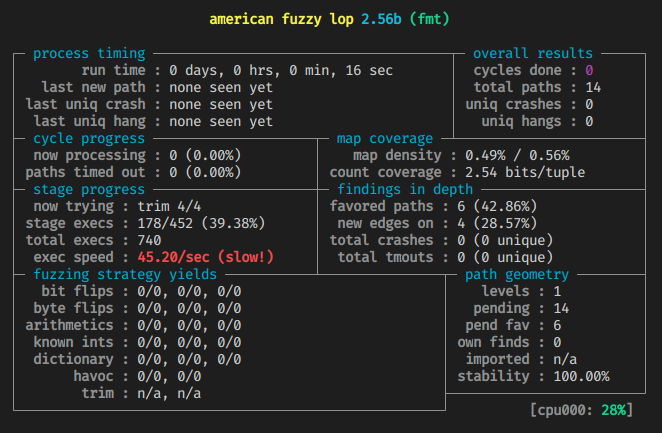
四、问题思考
第“三、1(2)”步骤的两种输入种子构造方法,对于 fuzzing 结果的影响(是否有影响?如果有,对最终获得的路径数量、路径数增长的速度等方面的具体影响)。
有影响:因为 AFL 可以通过启发式算法自动确定输入,但是如果直接用随机构造,最开始只能适应一般情况,而对特定程序的针对性不强。根据程序的输入构建一个高质量的语料库,能更好指导变异生成的随机输入,能发现更多路径数量,路径增长速度更快,就能获得更快的 Fuzzing 速度。
第“三、1”基于编译插桩的 fuzzing 与第“三、2”的基于 Qemu 动态插桩的 fuzzing,从基本原理和实验效果两方面的差异。
基本原理: 插桩分为动态插桩和静态插桩。基于编译插桩的 fuzzing 就是静态插桩,静态插桩发生在编译之前,PREPROCESS 这个阶段;基于 Qemu 插桩的 fuzzing 是动态插桩,在程序运行的时候发生,也就是每个 INPUTEVAL 阶段。因此,静态插桩相较于动态插桩有更优的开销,而动态插桩则更加容易对 DLL 进行插桩。除了基于源码的插桩,还有基于二进制文件的插桩,即未知源码的插桩技术。常见的动态插桩工具有 DynInst、Dynamo、RIOPIN、Valgrind、QEMU 等。
实验效果: 基于编译插桩的 fuzzing 的速度要远高于基于 Qemu 动态插桩的 fuzzing。但是基于 Qemu 动态插 桩的 fuzzing 不需要获取程序的源码,可执行文件就可以。
参考资料
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/128972800

